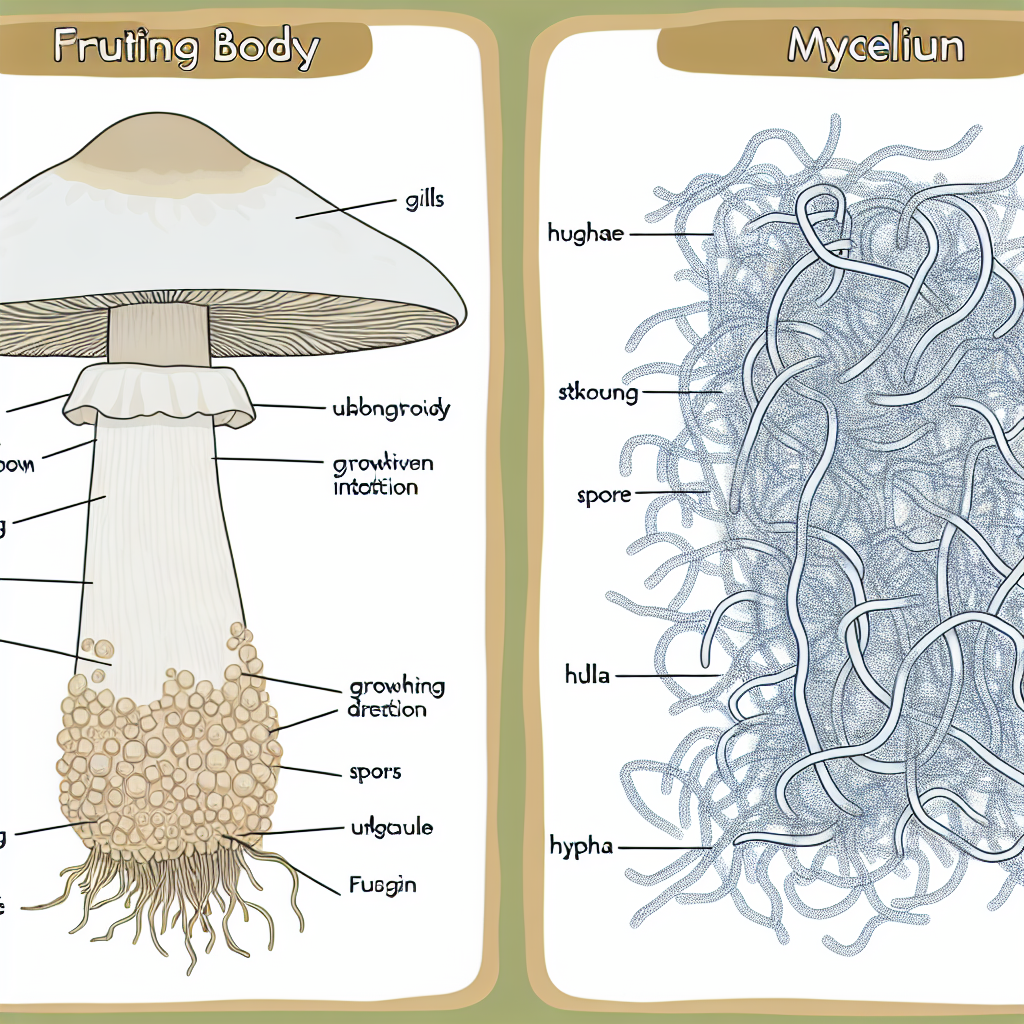
Fruiting Body vs. Mycelium: Understanding the Differences
The Rise of Medicinal Mushrooms
The world of medicinal mushrooms is rapidly growing, with more people turning to fungi for their natural healing properties. From immune system support and cognitive enhancement to anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial benefits, mushrooms offer a wealth of therapeutic potential. However, when choosing a mushroom supplement, one critical question arises: Should you opt for fruiting body-based products or mycelium-based ones?
Fungi grow in two primary stages—the mycelium and the fruiting body. The mycelium is the underground network of thread-like structures that absorb nutrients and support fungal growth. It acts as the mushroom’s root system, playing a role in decomposition and nutrient recycling. Conversely, the fruiting body is the visible part of the mushroom that produces spores, ensuring the survival of fungi.
In recent years, the debate over fruiting body vs. mycelium has sparked discussions among mycologists, health practitioners, and supplement manufacturers. Understanding the differences between these two components is crucial for making an informed choice when purchasing medicinal mushroom products.
Bioactive Compounds: Fruiting Body vs. Mycelium
Fruiting Body: Rich in Medicinal Compounds
The fruiting body of mushrooms is often considered superior in terms of bioactive compounds. A study published in the International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms found that fruiting bodies contain significantly higher concentrations of beta-glucans, which are known for their immune-boosting properties (Zhou et al., 2020). These compounds help activate macrophages and stimulate natural killer cells to fight pathogens.
Additionally, fruiting bodies are rich in triterpenes, such as ganoderic acids in Ganoderma lucidum (Reishi mushroom), which exhibit anti-inflammatory, liver-protective, and anticancer properties (Bishop et al., 2015). These medicinal compounds have been extensively studied, making fruiting body-based extracts highly sought after.
Mycelium: A Source of Unique Polysaccharides
While mycelium contains valuable polysaccharides and secondary metabolites, they are often found in lower concentrations than in fruiting bodies. Some studies suggest that mycelium grown on grain substrates may contain starchy filler compounds, which could dilute the concentration of bioactive ingredients (Hobbs, 2021).
However, certain species—such as Cordyceps militaris and Turkey Tail (Trametes versicolor)—produce unique bioactive compounds in their mycelial form. Mycelium has demonstrated immune-modulating effects, supporting its role in medicinal applications.
Scientific Research: How Do Fruiting Bodies and Mycelium Compare?
Clinical Studies Supporting Fruiting Bodies
✅ A 2019 study published in Oncotarget found that Ganoderma lucidum (Reishi mushroom) fruiting body extracts significantly inhibited cancer growth by inducing apoptosis and preventing tumor progression (Yu et al., 2019).
✅ A study on Lion’s Mane (Hericium erinaceus), published in Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, demonstrated that fruiting body extracts promote nerve regeneration and improve cognitive function. Compounds like erinacines and hericenones play a crucial role in brain health (Mori et al., 2021).
Clinical Studies Supporting Mycelium
✅ A 2014 study published in the International Journal of Biological Macromolecules found that Cordyceps militaris mycelium contains polysaccharides that enhance immune function by modulating cytokine production and increasing white blood cell activity (Kim et al., 2014).
✅ Turkey Tail mycelium has been studied for its cancer-supporting properties. A clinical trial conducted by the University of Minnesota found that Turkey Tail mycelium extracts helped cancer patients recover from chemotherapy by enhancing immune recovery and reducing inflammation (Torkelson et al., 2012).
Fruiting Body or Mycelium? Which One Should You Choose?
When selecting a medicinal mushroom supplement, the choice between fruiting body and mycelium depends on your needs and priorities:
Choose Fruiting Body-based Supplements If:
✔ You want higher concentrations of beta-glucans, triterpenes, and other medicinal compounds
✔ You seek potent immune-boosting, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects
✔ You prefer clinically studied extracts for cancer prevention, brain health, and overall wellness
Choose Mycelium-based Supplements If:
✔ You are interested in immune-modulating effects from specific mushroom species like Cordyceps militaris
✔ You want a faster, more sustainable cultivation process
✔ You prefer a full-spectrum approach (but be cautious of grain fillers)
Ultimately, selecting high-quality supplements that clearly indicate whether they use fruiting bodies, mycelium, or both is crucial.
Final Thoughts: Making an Informed Choice for Your Health
Both fruiting bodies and mycelium have their own unique benefits, but fruiting bodies are often recognized as the superior choice due to their higher concentrations of bioactive compounds.
As research continues, our understanding of mushroom-based therapies will only expand. To make the best decision for your health, choose supplements from trusted brands that transparently label their ingredient sources.
100 Word Summary:
When choosing a medicinal mushroom supplement, the decision between fruiting body and mycelium is crucial. Fruiting bodies generally contain higher concentrations of beneficial compounds like beta-glucans and triterpenes, making them a superior choice for immune-boosting, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects. However, mycelium also has unique polysaccharides and can provide immune-modulating benefits from specific species like Cordyceps militaris. Ultimately, selecting high-quality supplements that clearly label their ingredient sources is key to making an informed choice that aligns with your health goals.
References:
Bishop et al., 2015
Mori et al., 2021
Kim et al., 2014
Zhou et al., 2020
Hobbs, 2021

Dominic E. is a passionate filmmaker navigating the exciting intersection of art and science. By day, he delves into the complexities of the human body as a full-time medical writer, meticulously translating intricate medical concepts into accessible and engaging narratives. By night, he explores the boundless realm of cinematic storytelling, crafting narratives that evoke emotion and challenge perspectives. Film Student and Full-time Medical Writer for ContentVendor.com