Understanding How Chronic Inflammation Impacts Your Health
The immune system is active for a long time, which can cause chronic inflammation. This can then lead to the development of chronic illnesses. Inflammation is an important part of the body’s defense system; it helps fight off infections and accidents.
The Hidden Dangers of Long-Term Inflammatory Responses
On the other hand, inflammation that lasts for a long time can hurt good organs and tissues, which can lead to many illnesses, including heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, and cancer.
How Inflammation Contributes to Cardiovascular Problems
Damage to the body’s blood vessels is one way that long-term inflammation leads to long-term illnesses. When there is chronic inflammation, the blood vessels get swollen. This can cause atherosclerosis, a disease in which the arteries get clogged with plaque. This might make you more likely to get heart disease or a stroke.
The Connection Between Inflammation and Diabetes Risk
Insulin resistance is a situation in which the body’s cells stop responding to insulin. It can also be caused by long-term inflammation. This can cause your blood sugar to rise and cause type 2 diabetes to form. The cells in the pancreas that make insulin can also be hurt by inflammation, which makes diabetes even worse.
Inflammation’s Role in Cancer Development and Progression
In addition to these diseases, long-term inflammation can also make cancer more likely to happen. Damage and changes in DNA can happen over time because of chronic inflammation. This can cause cancer cells to grow. By making a setting that is good for their health, inflammation can also help cancer cells grow and spread.
Addressing Inflammation to Prevent Chronic Disease
In general, having chronic inflammation is a big reason why people get chronic illnesses. By learning more about how chronic inflammation causes disease, we can come up with better ways to stop and treat these diseases. Changing your food and getting more exercise, as well as taking medicines that target inflammation, can help lower your chance of getting chronic diseases that are linked to inflammation.
The Natural Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Medicinal Mushrooms
Medicinal mushrooms can help your body deal with inflammation in a healthy way. Inflammation is a complicated biological process that helps keep the body safe from getting sick or hurt. On the other hand, inflammation that lasts for a long time can cause many long-term diseases, like Alzheimer’s, arthritis, and cancer.
Key Compounds That Make Medicinal Mushrooms Effective
There are many chemicals in medicinal mushrooms that can help lower inflammation and support a healthy inflammatory reaction. Some of these chemicals are:
Understanding Beta-Glucans and Their Benefits
beta-glucans: These are a kind of carbohydrate that have been shown to lower inflammation by stopping the production of hormones that cause inflammation.
How Polysaccharides Support Your Immune Response
Another type of carbohydrate that has been shown to lower inflammation is polysaccharides. These carbs activate macrophages, which are cells that find and kill alien invaders.
The Anti-Inflammatory Power of Triterpenes
Triterpenes: Triterpenes are a type of plant substance that has been shown to help with fighting viruses and inflammation.
Lion’s Mane: A Special Mushroom for Nerve Health
They are called hericenones, and they are found in lion’s mane mushrooms. They have been shown to lower inflammation and help new nerve cells grow.
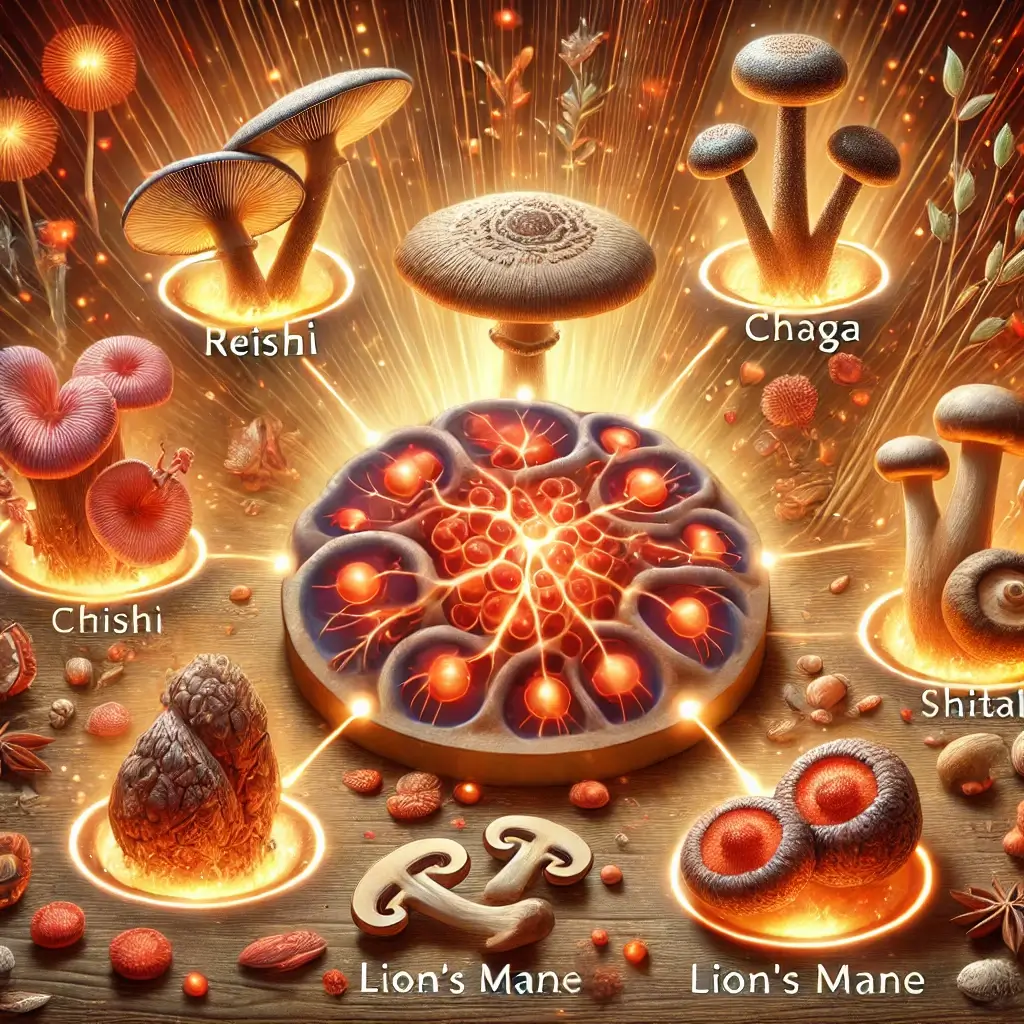
Popular Medicinal Mushrooms for Fighting Inflammation
Some of the most well-known mushrooms used to treat inflammation are
Reishi: The Stress-Reducing Adaptogen
It is known that reishi mushrooms can help the body deal with stress because they have features called adaptogens. It has also been shown that reishi mushrooms can lower inflammation and make the immune system work better.
Chaga: An Antioxidant Powerhouse for Heart Health
Chaga mushroom: A lot of antioxidants can be found in chaga mushrooms. Also, chaga mushrooms have been shown to lower inflammation and make heart health better.
Lion’s Mane: Enhancing Brain Function and Memory
Lion’s mane mushroom: These mushrooms are known to help the brain work better and remember things better. Also, lion’s mane mushrooms have been shown to lower swelling and help new nerve cells grow.
Shiitake: A Delicious Way to Boost Immunity
Shiitake mushroom: Shiitake mushrooms have a taste that is rich and high in umami. It has also been shown that shiitake mushrooms can lower inflammation and make the immune system work better.
Different Ways to Incorporate Medicinal Mushrooms
You can take medicinal mushrooms in many forms, such as pills, powders, drinks, and extracts. You can also put them in drinks and food.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals Before Use
If you want to take medical mushrooms to treat inflammation, you should first talk to your doctor. Some medicines may not work as well with medicinal mushrooms, so it’s important to know the risks and benefits before you take them.
The Limitations of Medicinal Mushrooms for Inflammation
Also, it’s important to know that medical mushrooms don’t get rid of inflammation. If you are having inflammation, you should see a doctor to find out what is causing it and get the right treatment.
References
- Elsayed, E. A., El Enshasy, H., Wadaan, M. A., & Aziz, R. (2014). Mushrooms: a potential natural source of anti-inflammatory compounds for medical applications. Mediators of inflammation, 2014, 805841.
- Guggenheim, A. G., Wright, K. M., & Zwickey, H. L. (2014). Immune Modulation From Five Major Mushrooms: Application to Integrative Oncology. Integrative Medicine: A Clinician’s Journal, 13(1), 32–44.
- Jayachandran, M., Xiao, J., & Xu, B. (2017). A Critical Review on Health Promoting Benefits of Edible Mushrooms through Gut Microbiota. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(9), 1934.
- Muszyńska, B., Grzywacz-Kisielewska, A., Kała, K., & Gdula-Argasińska, J. (2018). Anti-inflammatory properties of edible mushrooms: A review. Food Chemistry, 243, 373–381.
- Wasser, S.P. (2017). Medicinal Mushrooms in Human Clinical Studies. Part I. Anticancer, Oncoimmunological, and Immunomodulatory Activities: A Review. International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms, 19(4), 279–317.